A meaty first report by the UK parliamentary committee that’s been running an inquiry into online disinformation since fall 2017, including scrutinizing how people’s personal information was harvested from social media services like Facebook and used for voter profiling and the targeting of campaign ads — and whose chair, Damian Collins — is a member of the UK’s governing Conservative Party, contains one curious omission.
Among the many issues the report raises are privacy concerns related to a campaign app developed by a company called uCampaign — which, much like the scandal-hit (and now seemingly defunct) Cambridge Analytica, worked for both the Ted Cruz for President and the Donald J Trump for President campaigns — although in its case it developed apps for campaigns to distribute to supporters to gamify digital campaigning via a tool which makes it easy for them to ‘socialize’ (i.e. share with contacts) campaign messaging and materials.
The committee makes a passing reference to uCampaign in a section of its report which deals with “data targeting” and the Cambridge Analytica Facebook scandal, specifically — where it writes [emphasis ours]:
There have been data privacy concerns raised about another campaign tool used, but not developed, by AIQ [Aggregate IQ: Aka, a Canadian data firm which worked for Cambridge Analytica and which remains under investigation by privacy watchdogs in the UK, Canada and British Columbia]. A company called uCampaign has a mobile App that employs gamification strategy to political campaigns. Users can win points for campaign activity, like sending text messages and emails to their contacts and friends. The App was used in Donald Trump’s presidential campaign, and by Vote Leave during the Brexit Referendum.
The developer of the uCampaign app, Vladyslav Seryakov, is an Eastern Ukrainian military veteran who trained in computer programming at two elite Soviet universities in the late 1980s. The main investor in uCampaign is the American hedge fund magnate Sean Fieler, who is a close associate of the billionaire backer of SCL and Cambridge Analytica, Robert Mercer. An article published by Business Insider on 7 November 2016 states: “If users download the App and agree to share their address books, including phone numbers and emails, the App then shoots the data [to] a third-party vendor, which looks for matches to existing voter file information that could give clues as to what may motivate that specific voter. Thomas Peters, whose company uCampaign created Trump’s app, said the App is “going absolutely granular”, and will—with permission—send different A/B tested messages to users’ contacts based on existing information.”
What’s curious is that Collins’ Conservative Party also has a campaign app built by — you guessed it! — uCampaign, which the party launched in September 2017.
While there is nothing on the iOS and Android app store listings for the Conservative Campaigner app to identify uCampaign as its developer, if you go directly to uCampaign’s website the company lists the UK Conservative Party as one of it’s clients — alongside other rightwing political parties and organizations such as the (pro-gun) National Rife Association; the (anti-abortion) SBA List; and indeed the UK’s Vote Leave (Brexit) campaign, (the latter) as the DCMS report highlights.
uCampaign’s involvement as the developer of the Conservative Campaigner app was also confirmed to us (in June) by the (now former) deputy director & head of digital strategy for The Conservative Party, Anthony Hind, who — according to his LinkedIn profile — also headed up the party’s online marketing, between mid 2015 and, well, the middle of this month.
But while, in his initial response to us, Hind readily confirmed he was personally involved in the procurement of uCampaign as the developer of the Conservative Campaigner app, he failed to respond to any of our subsequent questions — including when we raised specific concerns about the privacy policy that the app had been using, prior to May 23 (just before the EU’s new GDPR data protection framework came into force on May 25 — a time when many apps updated their privacy polices as a compliance precaution related to the new data protection standard).
Since May 23 the privacy policy for the Conservative Campaigner app has pointed to the Conservative Party’s own privacy policy. However prior to May 23 the privacy policy was a literal (branded) copy-paste of uCampaign’s own privacy policy. (We know because we were tipped to it by a source — and verified this for ourselves.)
Here’s a screengrab of the exchange we had with Hind over LinkedIn — including his sole reply:
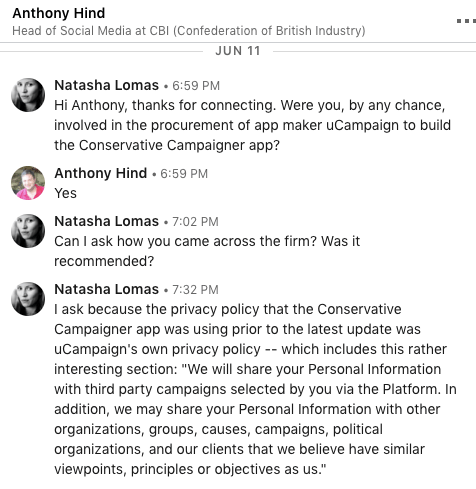
What looks rather awkward for the Conservative Party — and indeed for Collins, as DCMS committee chair, given the valid “privacy concerns” his report has raised around the use (and misuse/abuse) of data for political targeting — is that uCampaign’s privacy policy has, shall we say, a verrrrry ‘liberal’ attitude to sharing the personal data of app users (and indeed of any of their contacts it would have been able to harvest from their devices).
Here’s a taster of the data-sharing permissions this U.S. company affords itself over its clients’ users’ data [emphasis ours] — according to its own privacy policy:
CAMPAIGNS YOU SUPPORT AND ALIGNED ORGANIZATIONS
We will share your Personal Information with third party campaigns selected by you via the Platform. In addition, we may share your Personal Information with other organizations, groups, causes, campaigns, political organizations, and our clients that we believe have similar viewpoints, principles or objectives as us.
UCAMPAIGN FRIENDS
We may share your Personal Information with other users of the Platform, for example if they connect their address book to our services, or if they invite you to use our services via the Platform.
BUSINESS TRANSFERS
We may share your Personal Information with other entities affiliated with us for internal reasons, primarily for business and operational purposes. uCampaign, or any of its assets, including the Platform, may be sold, or other transactions may occur in which your Personal Information is one of the business assets of the transaction. In such case, your Personal Information may be transferred.
To spell it out, the Conservative Party paid for a campaign app that could, according to the privacy policy it had in place prior to May 23, have shared supporters’ personal data with organizations that uCampaign’s owners — who the DCMS committee states have close links to “the billionaire backer of SCL and Cambridge Analytica, Robert Mercer” — view as ideologically affiliated with their objectives, whatsoever those entities might be.
Funnily enough, the Conservative Party appears to have tried to scrub out some of its own public links to uCampaign — such as changing link for the developer website on the app listing page for the Conservative Campaigner app to the Conservative Party’s own website (whereas before it linked through to uCampaign’s own website).
As the veteran UK satirical magazine Private Eye might well say — just fancy that!
One of the listed “features” of the Conservative Campaigner app urges Tory supporters to: “Invite your friends to join you on the app!”. If any did, their friends’ data would have been sucked up by uCampaign too to further causes of its choosing.
The version of the Campaigner app listed on Google Play is reported to have 1,000+ installs (iOS does not offer any download ranges for apps) — which, while not in itself a very large number, could represent exponentially larger amounts of personal data should users’ contacts have been synced with the app where they would have been harvested by uCampaign.
We did flag the link between uCampaign and the Conservative Campaigner app directly to the DCMS committee’s press office — ahead of the publication of its report, on June 12, when we wrote:
The matter of concern here is that the Conservative party could itself be an unwitting a source of targeting data for rival political organizations, via an app that appears to offer almost no limits on what can be done with personal data.
Prior to the last update of the Conservative Campaigner app the privacy policy was simply the boilerplate uCampaign T&Cs — which allow the developer to share app users personal info (and phone book contacts) with “other organizations, groups, causes, campaigns, political organizations, and our clients that we believe have similar viewpoints, principles or objectives as us”.
That’s incredibly wide-ranging.
So every user’s phone book contacts (potentially hundreds of individuals per user) could have been passed to multiple unidentified organizations without people’s knowledge or consent. (Other uCampaign apps have been built for the NRA, and for anti-abortion organizations, for example.)
Even the current T&Cs allow for sharing with US suppliers.
Given the committee’s very public concerns about access to people’s data for political targeting purposes I am keen to know whether Mr Collins has any concerns about the use of uCampaign‘s app infrastructure by the Conservative party?
And also whether he is concerned about the lack of a robust data protection policy by his own party to ensure that valuable membership data is not simply passed around to unknown and unconnected entities — perhaps abroad, perhaps not — with zero regard for or accountability to the individuals in question.
Unfortunately this email (and a follow up) to the DCMS committee, asking for a response from Collins to our privacy concerns, went unanswered.
It’s also worth noting that the Conservative Party’s own privacy policy (which it’s now using for its Campaigner app) is pretty generous vis-a-vis the permissions it’s granting itself over sharing supporters’ data — including stating that it shares data with:
- The wider Conservative Party
- Business associates and professional advisers
- Suppliers
- Service providers
- Financial organisations – such as credit card payment providers
- Political organisations
- Elected representatives
- Regulatory bodies
- Market researchers
- Healthcare and welfare organisations
- Law enforcement agencies
The UK’s data watchdog recently found fault with pretty much all of the UK political parties’ when it comes to handling of voter data — saying it had sent warning letters to 11 political parties and also issued notices compelling them to agree to audits of their data protection practices.
Safe to say, it’s not just private companies that have been sticking their hand in the personal data cookie jar in recent years — the political establishment is facing plenty of awkward questions as regulators unpick where and how data has been flowing.
This is also not the only awkward story re: data privacy concerns related to a Tory political app. Earlier this year the then-minister in charge of the digital brief, Matt Hancock, launched a self-promotional, self-branded app intended for his constituents to keep up with news about Matt Hancock MP.
However the developers of the app (Disciple Media) initially uploaded the wrong privacy policy — and were forced to issue an amended version which did not grant the minister such non-specific and oddly toned rights to users’ data — such as that the app “may disclose your personal information to the Publisher, the Publisher’s management company, agent, rights image company, the Publisher’s record label or publisher (as applicable) and any other third parties, for use in conjunction with additional user promotions or offers they may run from time to time or in relation to the sale of other goods and services”.
Of course the Matt Hancock App was a PR initiative of (and funded by) an individual Conservative MP — rather than a formal campaign tool paid for by the Conservative Party and intended for use by hundreds (or even thousands) of Party activists for use during election campaigns.
So while there are two issues of Tory-related privacy concern here, only one loops back to the Conservative Party political organization itself.

Source: Tech Crunch
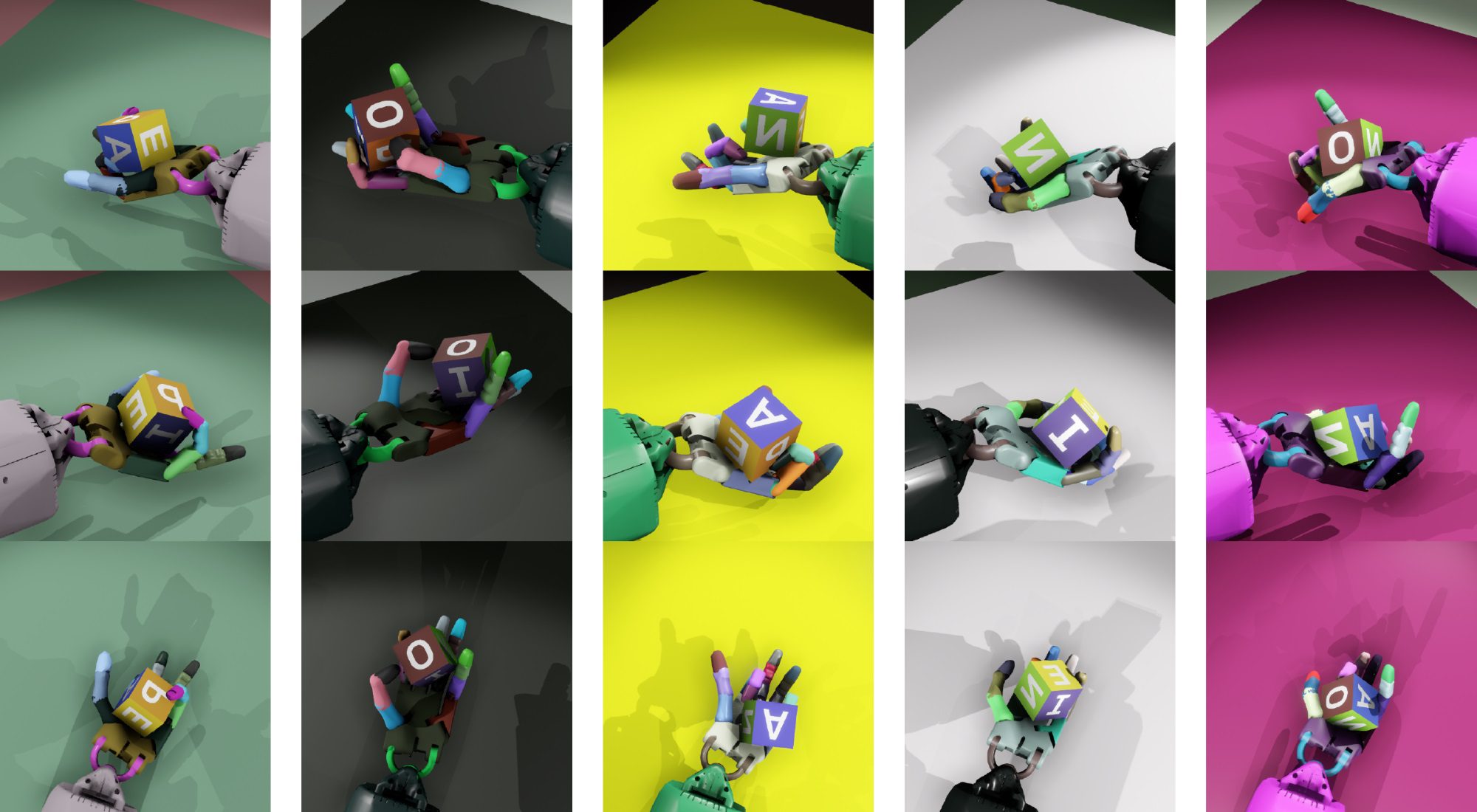





 The system, which they call Dactyl, was provided only with the positions of its fingers and three camera views of the object in-hand — but remember, when it was being trained, all this data is simulated, taking place in a virtual environment. There, the computer doesn’t have to work in real time — it can try a thousand different ways of gripping an object in a few seconds, analyzing the results and feeding that data forward into the next try. (The hand itself is a
The system, which they call Dactyl, was provided only with the positions of its fingers and three camera views of the object in-hand — but remember, when it was being trained, all this data is simulated, taking place in a virtual environment. There, the computer doesn’t have to work in real time — it can try a thousand different ways of gripping an object in a few seconds, analyzing the results and feeding that data forward into the next try. (The hand itself is a 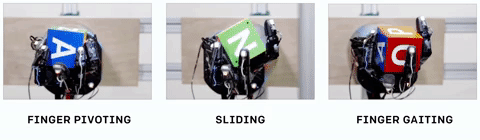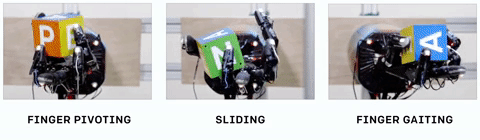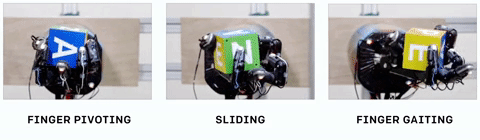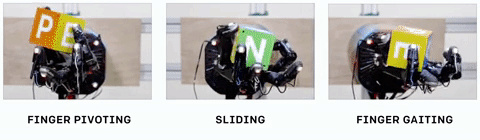 The things we do with our hands without even noticing, like turning an apple around to check for bruises or passing a mug of coffee to a friend, use lots of tiny tricks to stabilize or move the object. Dactyl recreated several of them, for example holding the object with a thumb and single finger while using the rest to spin to the desired orientation.
The things we do with our hands without even noticing, like turning an apple around to check for bruises or passing a mug of coffee to a friend, use lots of tiny tricks to stabilize or move the object. Dactyl recreated several of them, for example holding the object with a thumb and single finger while using the rest to spin to the desired orientation.